- About us
- Research expertise
- DIGITAL – Institut für Digitale Technologien
- MATERIALS – Institut für Sensorik, Photonik und Fertigungstechnologien
- ROBOTICS – Institut für Robotik und Flexible Produktion
- COREMED – Zentrum für Regenerative Medizin und Präzisionsmedizin
- HEALTH – Institut für Biomedizinische Forschung und Technologien
- LIFE – Institut für Klima, Energiesysteme und Gesellschaft
- POLICIES – Institut für Wirtschafts-, Sozial und Innovationsforschung
- Business areas
- Products & services
- Research infrastructure
- Beteiligungen
- Career
- Aktuelles
- Publications
- Kontakt zu uns
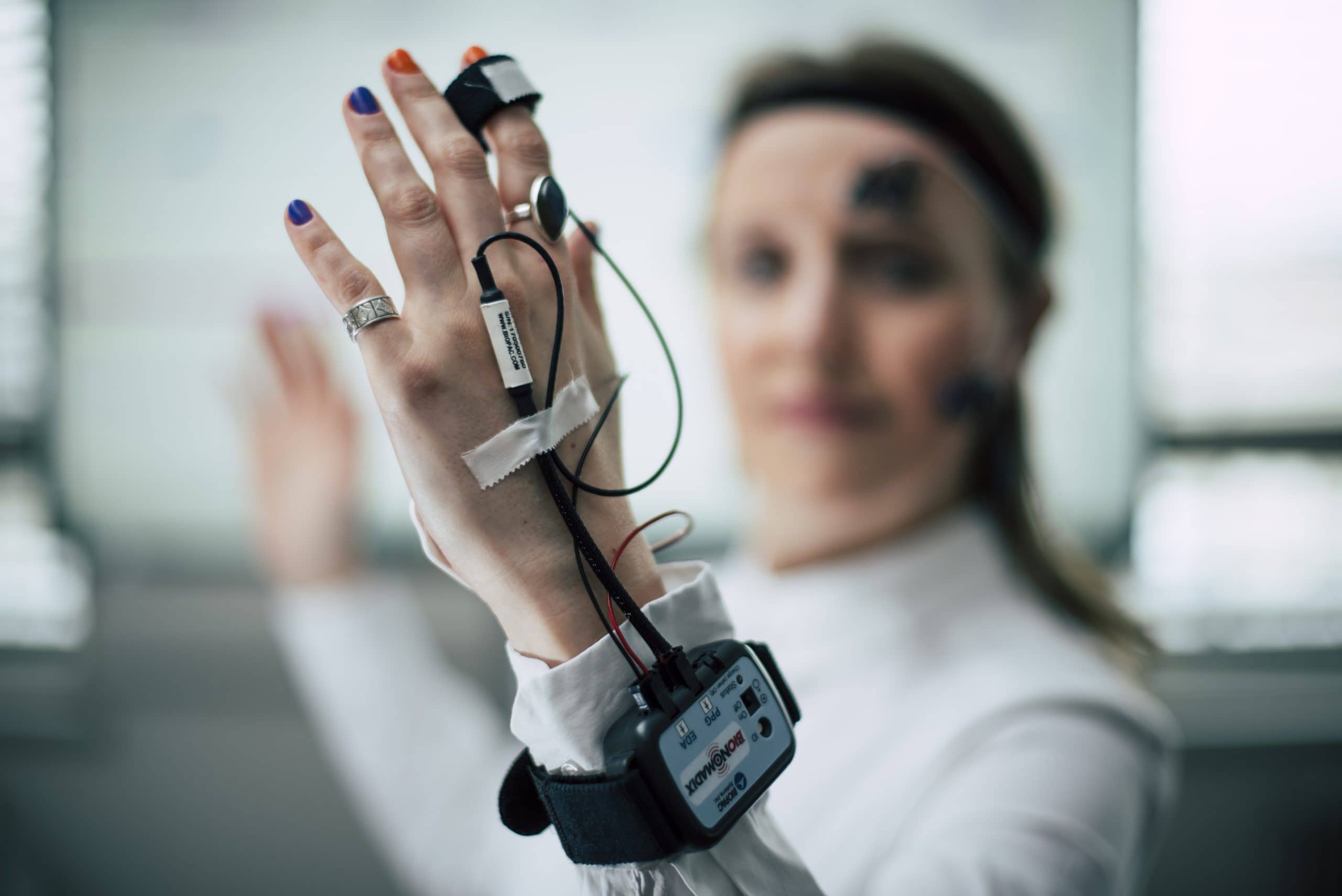
Human Factors laboratory
The laboratory combines state-of-the-art measurement technology with intelligent analysis software for prototype development and human factors and ergonomics studies.

Human factors focuses on people and their behaviour under stress and strong emotions, and is a key factor in the optimal adaptation of technical systems to people. The Human Factors Laboratory provides innovative measurements to analyse human attention, stress, emotion and behaviour.
Our team of experts develops digital biomarkers for psychophysiological assessment (cognitive screening for dementia, situational awareness for emergency services) and is active in the development and evaluation of assistance systems in the research area of AAL (Active & Assisted Living) and digital care. One focus is on information and communication technology and dementia, with the development of vision-based dementia training and VR-supported relaxation to increase cognitive reserves.
Equipment and measurement methods
The following instrumentation and platforms are used to develop new measurement technologies, simulate human-machine interactions, and develop intelligent multimodal interfaces for human-centred assistance systems:
- Eye tracking glasses: Attention studies are carried out for the application areas of marketing (attention in business areas), usability (mobile devices, control systems), human-machine interface (control centre, flight simulator), mobility (driver, driver assistance, driver safety, etc.) and performance diagnostics (emergency services, sports).
- Eye-tracking analysis: State-of-the-art, stationary, high-resolution eye-tracking technology enables precise on-screen studies for market research (product and shelf research), signage evaluation and video analysis.
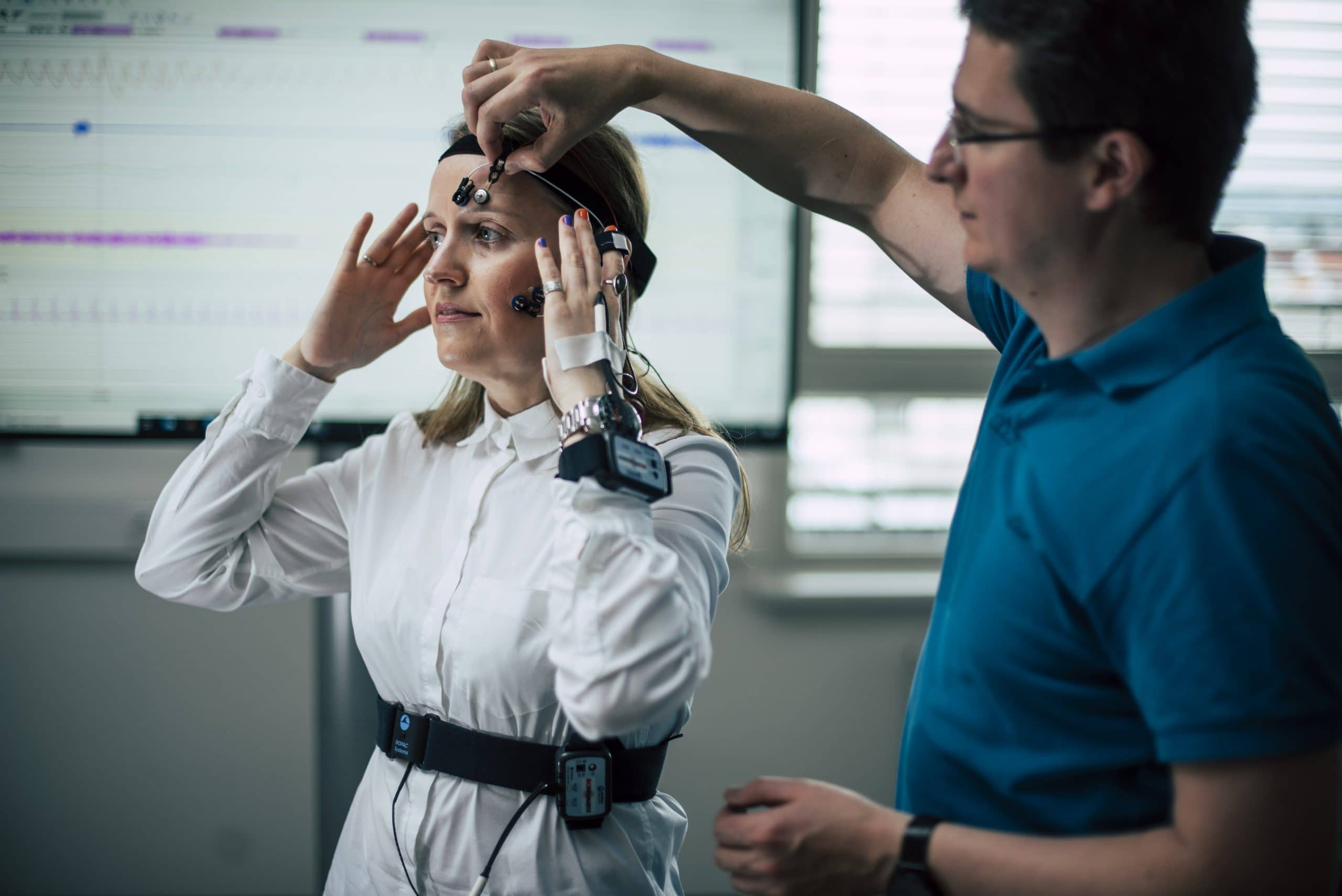
- Biosignal sensor technology: Digital, accurate and portable biosignal sensor technology can be used to objectively analyse physical and cognitive stress scenarios, especially in conjunction with eye-tracking analysis.
- Analyse von Emotionen: Für die Analyse von Emotionen werden einerseits Sensorik für Biosignale (Analyse der Gesichtsmuskulatur) und Videoanalyse (System Affectiva) angewendet.
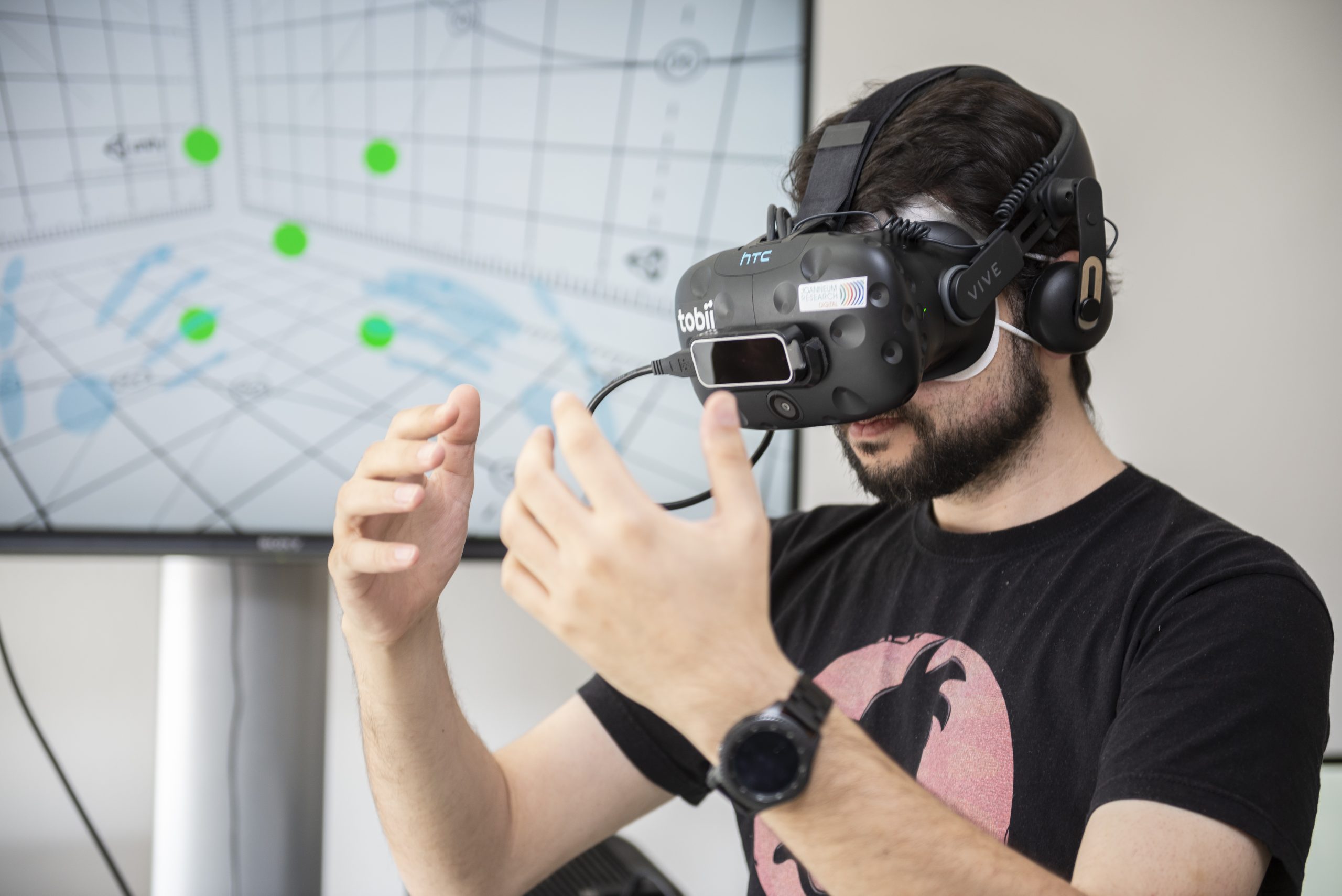
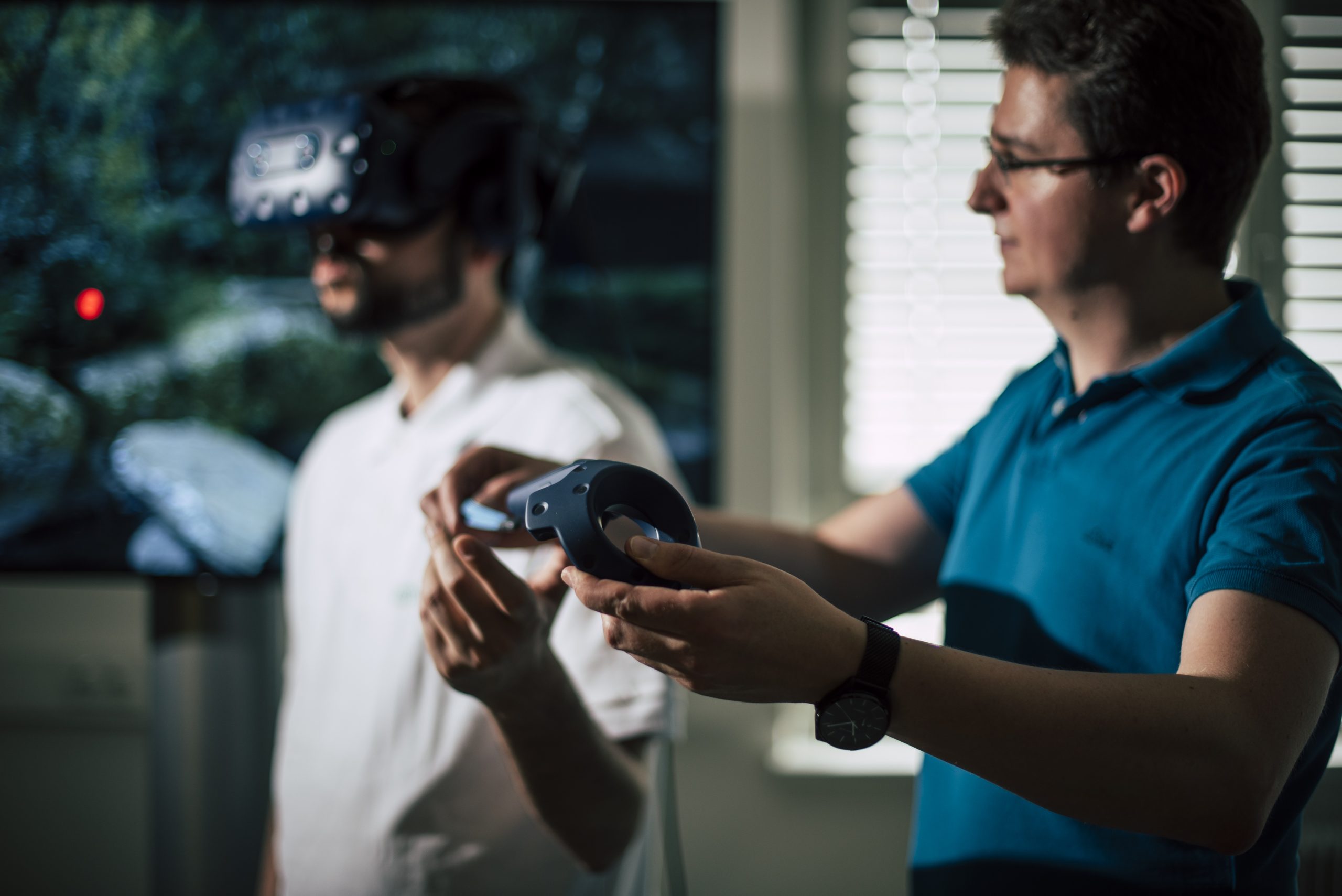
- VR and AR glasses: VR (virtual reality) and AR (augmented reality) glasses can be used to conduct targeted studies on the design of future work environments or interaction technologies, or to develop efficient interfaces for training, education, rehabilitation or process management.
- Motion capture: The motion capture system (OptiTrack) enables motion analysis for clinical research/rehabilitation with gait analysis, performance diagnostics in sports and, in conjunction with eye-tracking glasses, precise tracking of attention in space.
- Virtualizer: The Virtualizer makes it possible to experience mobility in virtual spaces in order to study orientation and situational awareness (emergency services, guidance systems).
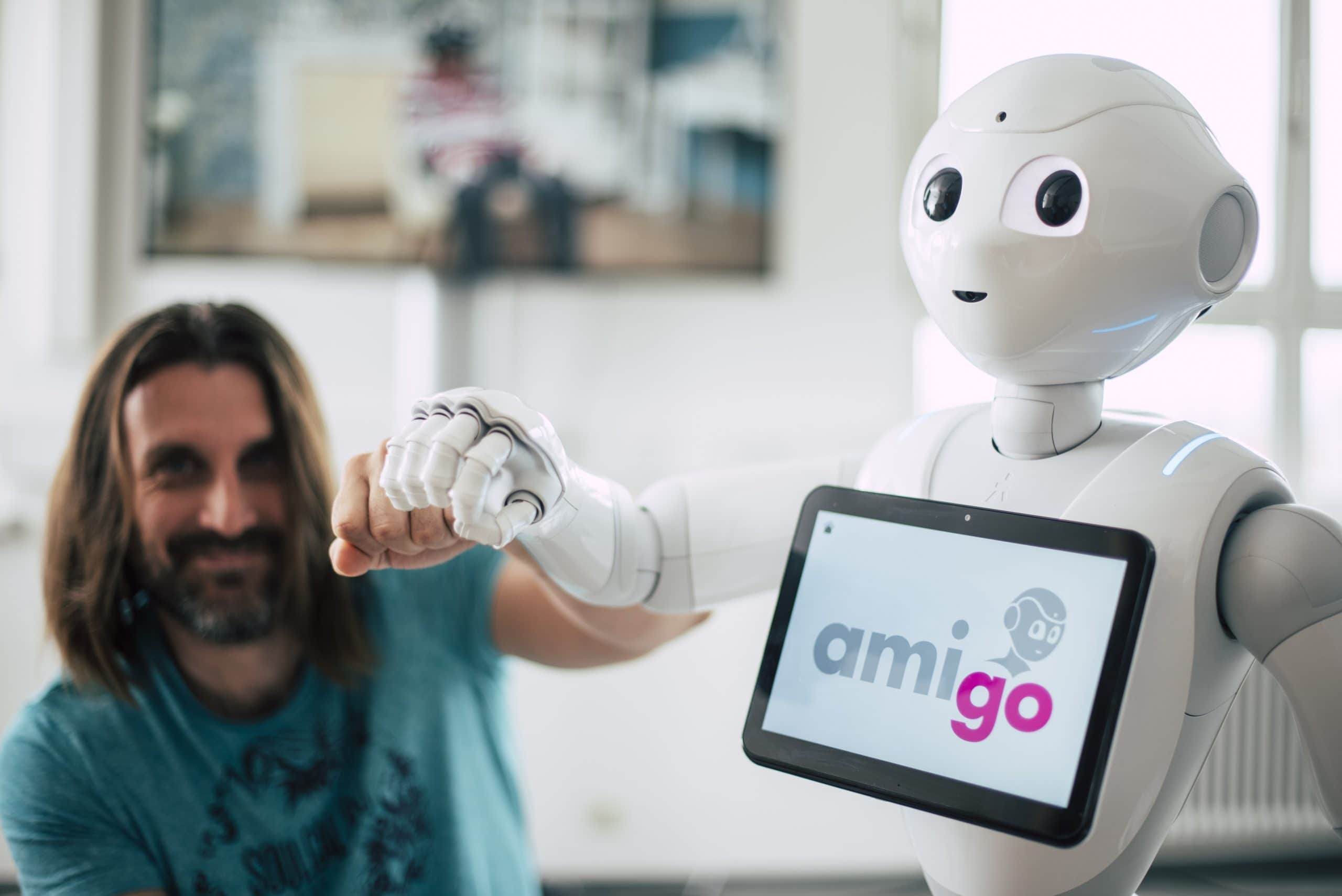
- Social robots: Social robots are used in the care sector (mobile, stationary) for motivation, entertainment and as interactive information stands; they can also be adapted for other applications.
Pepper as an "everyday companion"
The social robot Pepper, programmed as a "companion", is a joint product of the French company Aldebaran Robotics SAS and the Japanese telecommunications and media group SoftBank Mobile Corp. The social robot can speak, listen, gesticulate, dance and communicate with its interlocutor.
As Pepper cannot show facial expressions, other solutions have been used to detect emotions: The bright area around the pupil of his eyes can take on different LED colours. The effect of an emotional reaction is achieved through a sequence of colours. The robot can change the position of its head, shoulders and hands, and the movements it makes appear realistic because Pepper can use sensory equipment to move towards the conversation it hears in the room.
As part of the AMIGO project, our DIGITAL experts worked with partners to develop a multi-sensory, social robot platform designed to motivate people with dementia to perform multimodal training exercises on a daily basis in an entertaining way. The digital 'companion' allows personalised exercises to be carried out to stimulate cognitive processes and incorporate coordinative exercises and social aspects.

Your contact
Location
Das sagen unsere Kunden
Additional research infrastructure
DIGITAL has a hearing laboratory equipped to international standards (ITU-R BS 1116-1).
In our AI Lab, we provide human and computational resources for research and development of state-of-the-art AI (neural network) models.
We develop innovative software and hardware solutions for satellite radio.
We carry out experiments in optical metrology, optical spectroscopy and machine vision.
High-precision 3D measurement systems enable the research and implementation of innovative solutions for the automated creation of digital twins.
For innovative satellite communications, our infrastructure includes antennas in the Q/V band (40/50 GHz) and W band (71-76 GHz).
The IoT Innovation Space is both a physical and virtual space to help you achieve digital transformation with design thinking, IoT and AI.
SHAPING THE FUTURE, TOGETHER
JOANNEUM RESEARCH provides innovation and technology services in the field of applied research. As a research company working on behalf of various federal provinces and regions in Austria, our expertise shapes the development of our modern society and economy – sustainably, and always with a focus on people. As a multidisciplinary team working in a flexible set-up that fosters innovation, we always live up to the highest social and scientific standards.